Danh sách bài viết trong series Học Kubernetes Từ Cơ Bản Đến Chứng Chỉ CKAD
- Lộ Trình Học Kubernetes Từ Cơ Bản Đến Chứng Chỉ CKAD
- Bài 1: Giới Thiệu Kubernetes Và Khái Niệm Cluster Cho CKAD
- Bài 2: Cài Đặt Minikube Và sử dụng kubectl Cơ Bản
- Bài 3: Quản Lý Pod Cơ Bản (Create, Delete, Describe)
- Bài 4: Sử Dụng ConfigMap Và Secret Trong YAML
- Bài 5: Quản Lý Environment Variables Và Command/Args
- Bài 6: Cấu Hình Deployment Và Replica Set
- Bài 7: Thiết Kế Pod Với Nhiều Container
- Bài 8: Sử Dụng Sidecar Và Init Container
- Bài 9: Chia Sẻ Tài Nguyên Giữa Các Container
- Bài 10: Giám Sát Log Và Events Với kubectl logs
- Bài 11: Debug Pod Với kubectl describe Và exec
- Bài 12: Tối Ưu Pod Với Resource Limits Và Requests
- Bài 13: Sử Dụng Liveness Và Readiness Probes
- Bài 14: Tối Ưu Hóa Pod Với HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)
- Bài 15: Cấu Hình Service (ClusterIP, NodePort)
- Bài 16: Sử Dụng Ingress Và Network Policy
- Bài 17: Quản Lý DNS Và Load Balancing Trong Kubernetes
- Bài 18: Sử Dụng Volume (emptyDir, hostPath)
- Bài 19: Cấu Hình Persistent Volume Và Persistent Volume Claim
- Bài 20: Tổng Kết, Mẹo Thi CKAD, Bài Tập Thực Hành Cuối
Sau khi đã học cách sử dụng sidecar và init container trong Bài 8, chúng ta sẽ kết thúc domain Multi-Container Pods (chiếm 18% trọng số trong kỳ thi CKAD) bằng việc tìm hiểu cách chia sẻ tài nguyên giữa các containers trong cùng Pod. Đây là nền tảng làm nên sức mạnh của multi-container design, cho phép các containers giao tiếp và chia sẻ data một cách hiệu quả mà không cần network overhead hoặc storage external phức tạp.
Bài viết này tập trung vào các cơ chế chia sẻ như network namespace, storage volumes, IPC (Inter-Process Communication), và các namespace khác. Trong CKAD, domain này yêu cầu bạn thành thạo việc cấu hình shared resources để giải quyết các task như mount volume chung cho sidecar đọc logs từ app, hoặc sử dụng localhost để giao tiếp giữa containers. Bạn có thể gặp task kiểu debug Pod nơi containers không share đúng volume, hoặc viết YAML để init container populate data cho app. Chúng ta sẽ sẽ đi và các phần chi tiết để bạn nắm vững, từ lý thuyết đến troubleshoot.
Lý Do Chia Sẻ Tài Nguyên Giữa Các Container
Trong một Pod multi-container, các containers được thiết kế để hoạt động như một đơn vị cohesive, tương tự các process trong cùng máy ảo. Kubernetes tận dụng Linux namespaces và cgroups để isolate containers, nhưng cho phép chia sẻ một số namespaces để hỗ trợ interaction. Điều này giúp:
- Giảm latency: Giao tiếp qua localhost thay vì network full (ví dụ: app gửi request đến sidecar proxy trên port 8080).
- Chia sẻ data: Sử dụng volumes để read/write files chung, tránh duplicate storage hoặc external mounts.
- Tích hợp chặt chẽ: Sidecar có thể monitor app qua shared process signals (IPC) hoặc PID namespace.
- Efficiency: Giảm resource overhead so với multi-Pods (mỗi Pod có IP riêng, network policies phức tạp hơn).
- Patterns hỗ trợ: Enable sidecar (share logs qua volume), ambassador (share network cho proxy), adapter (transform data chung).
Tuy nhiên, chia sẻ cũng có rủi ro: Một container crash có thể ảnh hưởng toàn Pod, hoặc conflict permissions trên shared volume. Trong CKAD, hiểu phần này giúp bạn debug nhanh, ví dụ: Tại sao sidecar không thấy file từ app? (Sai mountPath hoặc volume type).
Các Loại Tài Nguyên Có Thể Chia Sẻ
Kubernetes cho phép chia sẻ nhiều loại namespaces và resources. Dưới đây là các loại chính, với giải thích và ví dụ.
1. Network Namespace
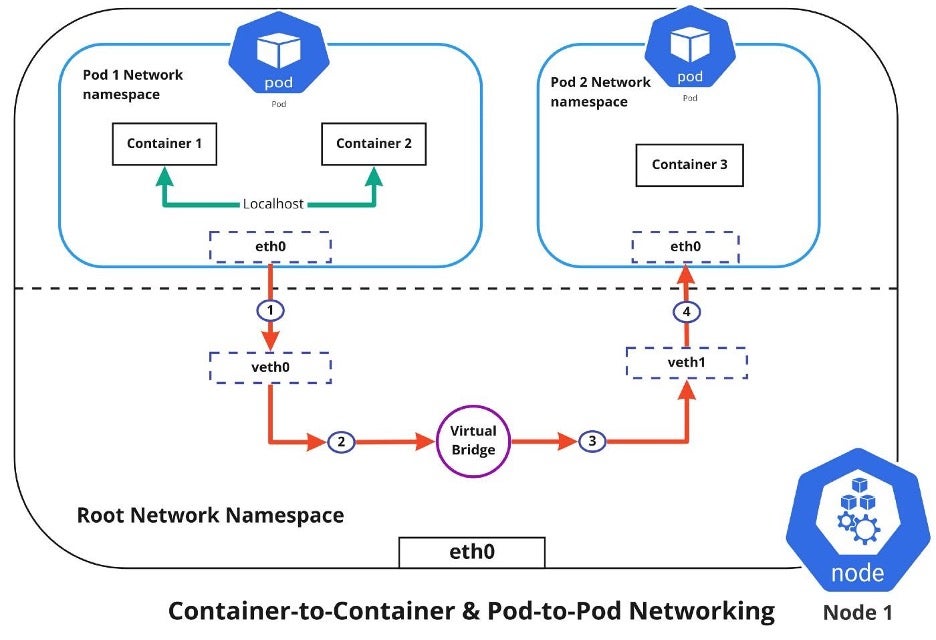
Tất cả containers trong Pod chia sẻ cùng network namespace: Cùng IP, ports, và localhost. Điều này cho phép:
- Giao tiếp nội bộ qua localhost:port mà không cần Service hoặc DNS.
- Sidecar proxy traffic: App connect localhost:8080, sidecar forward đến external.
- Debug: Exec vào một container để curl localhost từ container khác.
Ví dụ: App container listen port 80, sidecar curl localhost:80 để health check.
Dưới đây là diagram network namespace sharing trong Pod, minh họa cách containers dùng cùng eth0 interface.
2. Storage (Volumes)
Chia sẻ storage qua volumes là phổ biến nhất, cho phép containers mount cùng volume để read/write files. Types volumes cho sharing:
- emptyDir: Temporary, xóa khi Pod die; lý tưởng cho cache/logs.
- hostPath: Mount từ node host, share giữa containers nhưng không persistent qua Pod restarts.
- configMap/Secret: Mount config như files, share env-like data.
- persistentVolume: Cho data persistent, nhưng trong multi-container thường dùng emptyDir cho intra-Pod.
Ví dụ: App write logs vào /var/log/app.log trên volume, sidecar đọc và ship.
Dưới đây là diagram shared volume giữa containers trong Pod, cho thấy read/write flow.
3. IPC Namespace
IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace cho phép chia sẻ message queues, semaphores, shared memory. Default không share, nhưng enable bằng spec.shareProcessNamespace: true (chia PID namespace nữa).
- Use case: Containers cần signal nhau (kill process), hoặc share memory cho performance (rare in containers).
- Rủi ro: Security issues nếu không trust containers.
4. PID Namespace (Với ShareProcessNamespace)
Khi enable shareProcessNamespace: true, containers thấy processes của nhau qua /proc, có thể ps aux từ một container thấy tất cả.
- Use case: Debug toàn Pod, hoặc sidecar monitor app processes.
- Ví dụ: Sidecar dùng
killđể signal app container.
5. UTS Namespace
Containers chia sẻ hostname và domainname (UTS namespace), nên hostname giống nhau.
6. Environment Variables Và Config
Không trực tiếp share env vars, nhưng có thể dùng Downward API hoặc ConfigMap để inject chung.
Bảng Tóm Tắt Các Loại Chia Sẻ
| Tài Nguyên | Cách Chia Sẻ | Ví Dụ Use Case | YAML Config |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Namespace | Default chia sẻ | App-sidecar giao tiếp localhost:port | Không cần, auto |
| Storage Volumes | Mount cùng volume vào volumeMounts | Share logs/files giữa app và sidecar | spec.volumes & volumeMounts |
| IPC Namespace | Default isolate, enable shareProcessNamespace | Share message queues | spec.shareProcessNamespace: true |
| PID Namespace | Enable shareProcessNamespace | Monitor processes từ sidecar | spec.shareProcessNamespace: true |
| UTS Namespace | Default chia sẻ | Chung hostname | Auto |
| Env Vars | Không direct, dùng ConfigMap chung | Inject config cho tất cả containers | envFrom: configMapRef |
Dưới đây là diagram khác về shared volume, minh họa multi-Pod nhưng focus vào intra-Pod sharing.
Cấu Hình Chia Sẻ Tài Nguyên Trong YAML
Ưu tiên declarative YAML. Dưới đây là ví dụ chi tiết.
Ví Dụ 1: Chia Sẻ Volume (Storage)
Pod với app và sidecar share emptyDir cho logs:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: shared-volume-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: app-container
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: shared-logs
mountPath: /var/log/app
- name: sidecar-container
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c", "tail -f /logs/access.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: shared-logs
mountPath: /logs
volumes:
- name: shared-logs
emptyDir: {}App write vào /var/log/app, sidecar đọc từ /logs.
Ví Dụ 2: Chia Sẻ Network (Localhost)
App listen 80, sidecar curl localhost:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: shared-network-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: app-container
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- name: client-sidecar
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c", "while true; do wget -q -O- localhost:80; sleep 10; done"]Sidecar access app qua localhost:80.
Ví Dụ 3: Chia Sẻ Process Namespace
Enable shareProcessNamespace để sidecar thấy processes của app:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: shared-process-pod
spec:
shareProcessNamespace: true
containers:
- name: app-container
image: nginx
- name: monitor-sidecar
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c", "ps aux; sleep infinity"]Sidecar chạy ps aux thấy nginx processes.
Các Lệnh Kubectl Để Quản Lý Và Debug Chia Sẻ
- Describe Pod:
kubectl describe pod shared-volume-pod(xem volumeMounts, events nếu mount fail). - Exec để check share:
kubectl exec -it shared-volume-pod -c sidecar-container -- ls /logs(xem files từ app). - Logs từ sidecar:
kubectl logs shared-volume-pod -c sidecar-container. - Check network:
kubectl exec -it shared-network-pod -c client-sidecar -- curl localhost:80. - Debug process:
kubectl exec -it shared-process-pod -c monitor-sidecar -- ps aux(thấy all processes). - Port-forward để test:
kubectl port-forward pod/shared-network-pod 8080:80(access app từ local).
Liên Hệ Với Chứng Chỉ CKAD
Domain Multi-Container Pods (18%) thường yêu cầu cấu hình shared resources, chiếm phần lớn task. Ví dụ:
- Mount volume chung cho init container write và app read.
- Sử dụng localhost để sidecar proxy requests từ app.
- Debug sharing fail (sai mountPath, permissions).
Mẹo thi:
- Kiểm tra permissions: Containers khác user/group có thể gây write fail; dùng init để chown.
- Thời gian: 5-8 phút/task; verify bằng exec ls/cat hoặc curl localhost.
- Nhớ: Network luôn share, volume cần explicit mount.
- Luyện:
kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.emptyDircho docs. - Tránh shareProcessNamespace trừ khi yêu cầu, vì security.
Thực Hành Thực Tế Trên Minikube
- Tạo Pod shared volume: Sao chép YAML volume vào
shared-vol.yaml, apply:kubectl apply -f shared-vol.yaml. - Kiểm tra:
kubectl exec -it shared-volume-pod -c app-container -- echo "Test log" > /var/log/app/test.log kubectl exec -it shared-volume-pod -c sidecar-container -- cat /logs/test.log # Thấy "Test log" - Tạo Pod shared network: Apply YAML network.
- Kiểm tra network:
kubectl logs shared-network-pod -c client-sidecar # Thấy wget output từ nginx - Tạo Pod shared process: Apply YAML process.
- Kiểm tra process:
kubectl exec -it shared-process-pod -c monitor-sidecar -- ps aux # Thấy nginx worker - Cleanup:
kubectl delete pod shared-volume-pod shared-network-pod shared-process-pod.
Nếu fail, dùng describe check events (ví dụ: mount error).
Kết Luận
Bài này mình đã hướng dẫn chi tiết chia sẻ tài nguyên giữa containers, từ network đến volumes. Bạn giờ có thể thiết kế multi-container Pods hiệu quả, hoàn tất domain Multi-Container Pods cho CKAD. Tiếp theo, ở Bài 10: Giám Sát Log Và Sự Kiện Với kubectl logs, chúng ta sẽ bước vào domain Observability để học debug. Viết muốn rụng cái tay may mà tính từ đầu một format cũng nhẹ nhàng hơn :))