Danh sách bài viết trong series Học Kubernetes Từ Cơ Bản Đến Chứng Chỉ CKAD
- Lộ Trình Học Kubernetes Từ Cơ Bản Đến Chứng Chỉ CKAD
- Bài 1: Giới Thiệu Kubernetes Và Khái Niệm Cluster Cho CKAD
- Bài 2: Cài Đặt Minikube Và sử dụng kubectl Cơ Bản
- Bài 3: Quản Lý Pod Cơ Bản (Create, Delete, Describe)
- Bài 4: Sử Dụng ConfigMap Và Secret Trong YAML
- Bài 5: Quản Lý Environment Variables Và Command/Args
- Bài 6: Cấu Hình Deployment Và Replica Set
- Bài 7: Thiết Kế Pod Với Nhiều Container
- Bài 8: Sử Dụng Sidecar Và Init Container
- Bài 9: Chia Sẻ Tài Nguyên Giữa Các Container
- Bài 10: Giám Sát Log Và Events Với kubectl logs
- Bài 11: Debug Pod Với kubectl describe Và exec
- Bài 12: Tối Ưu Pod Với Resource Limits Và Requests
- Bài 13: Sử Dụng Liveness Và Readiness Probes
- Bài 14: Tối Ưu Hóa Pod Với HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)
- Bài 15: Cấu Hình Service (ClusterIP, NodePort)
- Bài 16: Sử Dụng Ingress Và Network Policy
- Bài 17: Quản Lý DNS Và Load Balancing Trong Kubernetes
- Bài 18: Sử Dụng Volume (emptyDir, hostPath)
- Bài 19: Cấu Hình Persistent Volume Và Persistent Volume Claim
- Bài 20: Tổng Kết, Mẹo Thi CKAD, Bài Tập Thực Hành Cuối
Sau khi đã khám phá cách chia sẻ tài nguyên giữa các container trong Bài 9, chúng ta sẽ bước vào domain Observability (chiếm 10% trọng số trong kỳ thi CKAD). Bài này tập trung vào việc giám sát logs và events bằng lệnh kubectl logs, cùng với cách sử dụng kubectl get events để theo dõi sự kiện cluster. Đây là công cụ thiết yếu để debug ứng dụng, xác định lỗi runtime, và hiểu hành vi của Pods/containers.
Domain Observability trong CKAD yêu cầu bạn thành thạo việc truy xuất logs để troubleshoot, chẳng hạn như xem logs từ container crash hoặc theo dõi events để debug Pod không schedule. Trong kỳ thi, bạn có thể gặp task như lấy logs từ Pod multi-container, filter events theo namespace, hoặc debug CrashLoopBackOff qua logs (đến đây là bắt đầu khoai hơn tý này).
Logs Trong Kubernetes Là Gì Và Cách Quản Lý
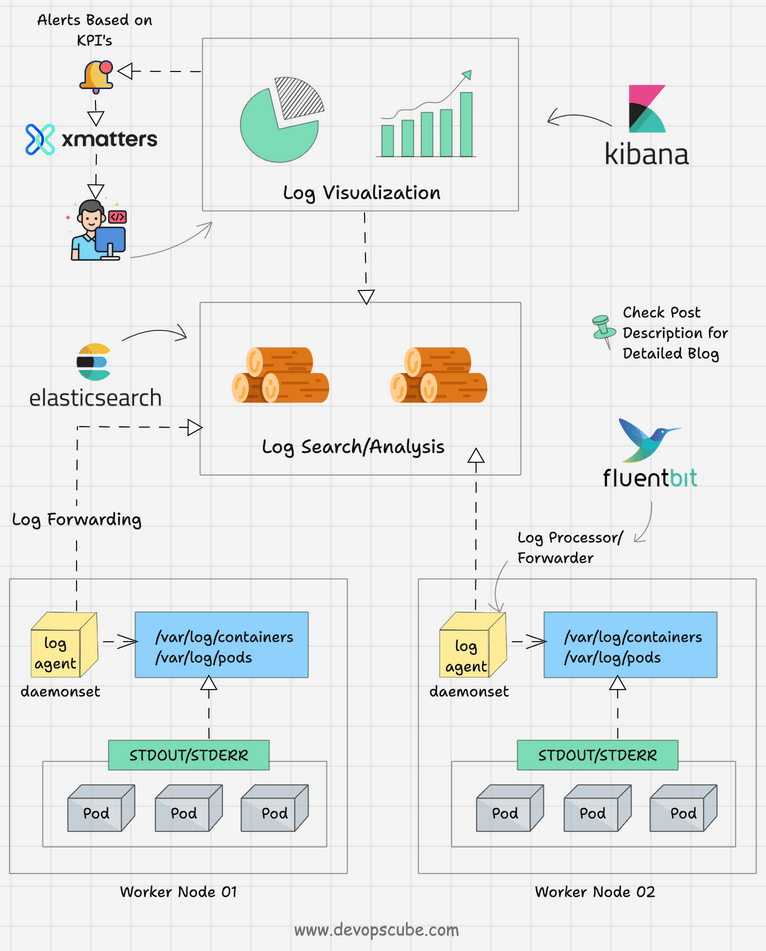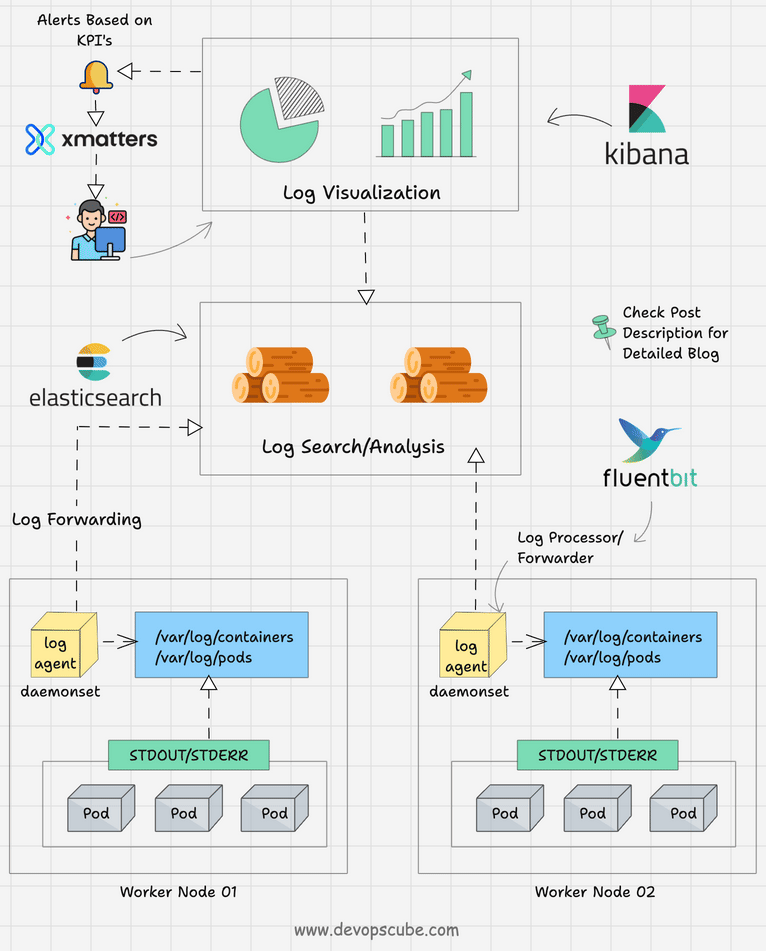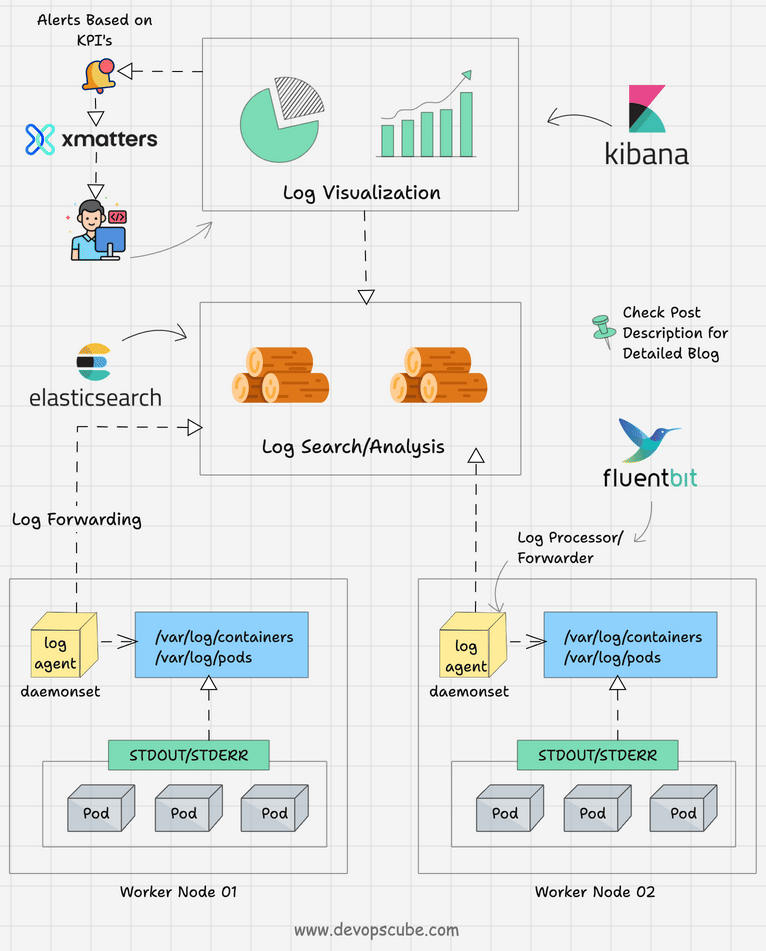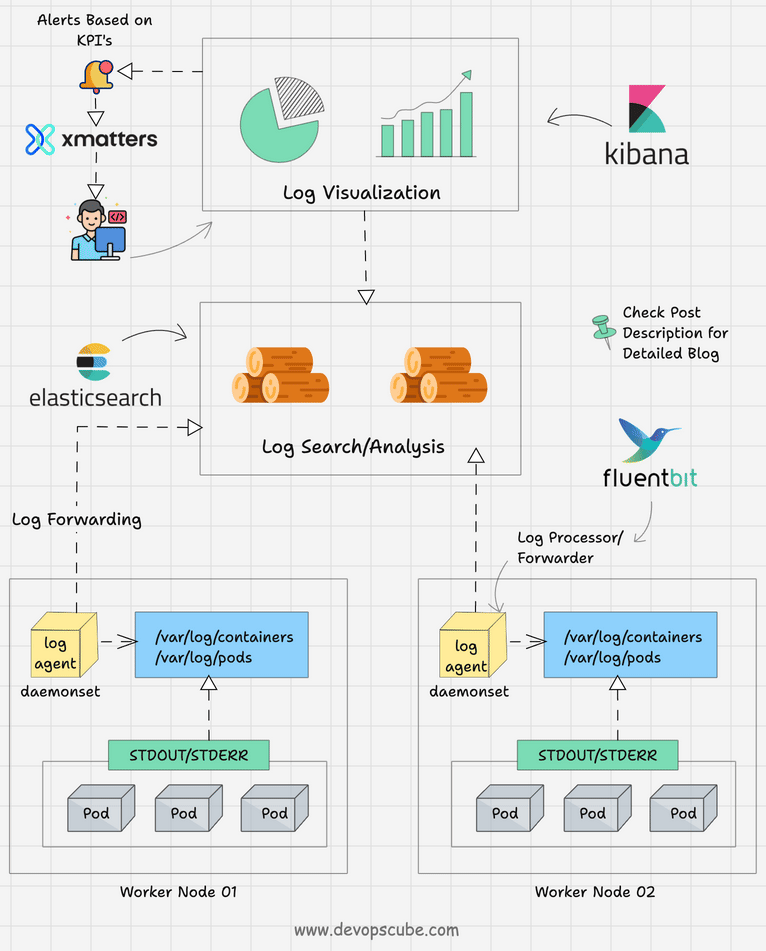
Logs là output từ stdout/stderr của containers, bao gồm messages ứng dụng, errors, hoặc debug info. Kubernetes không lưu logs persistent (trừ khi config), mà forward chúng từ container runtime (như containerd) đến kubelet, rồi có thể aggregate qua sidecar hoặc daemon như Fluentd.
Cấu trúc logs:
- Container logs: Lưu tại /var/log/containers trên node, symlink đến /var/log/pods.
- Pod logs: Aggregate từ tất cả containers trong Pod.
- Cluster logs: Bao gồm kubelet, API server logs, nhưng focus CKAD là Pod/container logs.
Cách quản lý logs:
- Basic:
kubectl logslấy trực tiếp từ kubelet. - Advanced: Sidecar container ship logs đến ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) hoặc tools như Loki.
- Best practice: Không write logs vào files trong container (trừ volume), dùng stdout để dễ aggregate.
Trong CKAD, hiểu logs giúp debug nhanh, ví dụ: Xem tại sao container exit code 1.
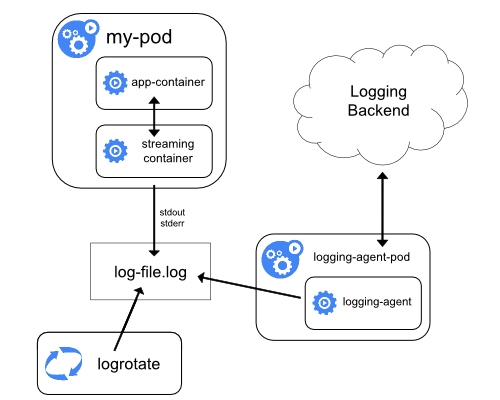
Dưới đây là diagram kiến trúc logging từ tài liệu chính thức Kubernetes, minh họa cách logs từ container streaming đến backend qua sidecar.
Events Trong Kubernetes Là Gì
Events là objects ghi lại các sự kiện xảy ra trong cluster, như Pod created, scheduled, image pull fail, hoặc node not ready. Chúng lưu trong etcd với TTL (default 1 giờ), giúp trace vấn đề hệ thống.
Types events:
- Normal: Thông tin thông thường (e.g., Pulling image).
- Warning: Lỗi tiềm ẩn (e.g., FailedScheduling).
Events liên kết với objects (Pod, Node) qua involvedObject field.
Trong CKAD, events hữu ích để debug tại sao Pod Pending hoặc CrashLoopBackOff.
Dưới đây là ví dụ output kubectl get events.
Các Lệnh Kubectl Để Giám Sát Logs
kubectl logs lấy logs từ Pod/container. Syntax cơ bản: kubectl logs <pod-name> [-c <container>] [options].
Lệnh Cơ Bản Và Options
- Lấy logs Pod đơn container:
kubectl logs my-pod. - Chỉ định container:
kubectl logs my-pod -c sidecar(bắt buộc cho multi-container). - Follow realtime:
kubectl logs -f my-pod(tail logs nhưtail -f). - Logs từ previous container:
kubectl logs my-pod --previous(nếu container crash và restart). - Limit lines:
kubectl logs my-pod --tail=50(last 50 lines). - Timestamp:
kubectl logs my-pod --timestamps(thêm time prefix). - Since time:
kubectl logs my-pod --since=1hhoặc--since-time=2023-10-24T00:00:00Z. - All containers:
kubectl logs my-pod --all-containers(aggregate từ tất cả).
Ví dụ: Debug CrashLoopBackOff: kubectl logs my-pod --previous -c app.
Các Lệnh Kubectl Để Giám Sát Events
- Liệt kê events:
kubectl get events(default namespace). - All namespaces:
kubectl get events -A. - Watch realtime:
kubectl get events --watch. - Sort by time:
kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp. - Output format:
kubectl get events -o wide(thêm details). - Filter: Dùng
kubectl get events -l app=myapp(label selector).
Ví dụ: Debug Pod fail: kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp | grep my-pod.
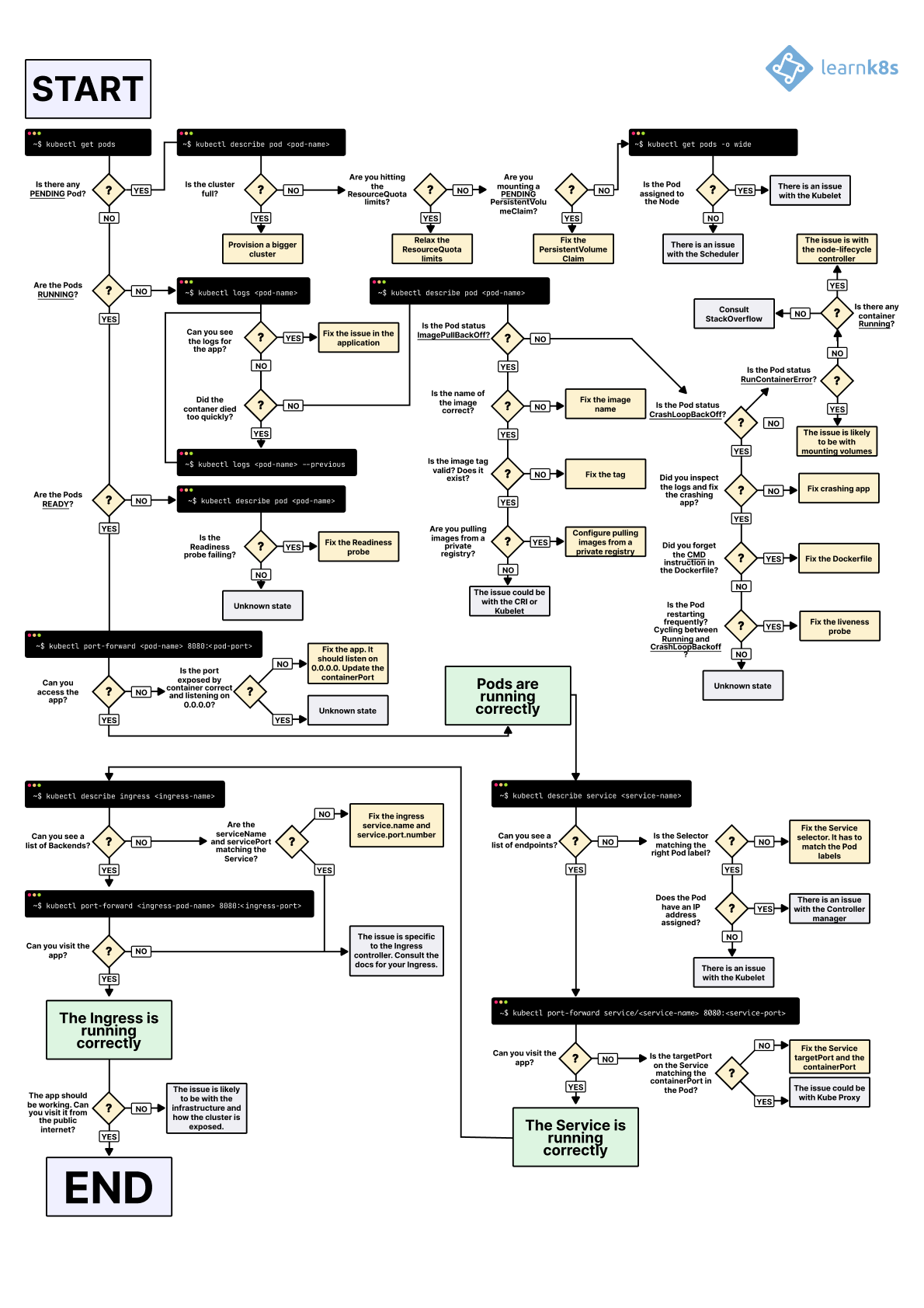
Dưới đây là flowchart troubleshooting Kubernetes với logs và events, hữu ích cho debug flow.
Bảng Cheat Sheet Lệnh Logs Và Events
| Lệnh | Mô tả | Ví dụ |
|---|---|---|
| kubectl logs [pod] | Lấy logs Pod cơ bản | kubectl logs nginx-pod |
| kubectl logs -f pod -c [cont] | Follow logs container cụ thể | kubectl logs -f nginx-pod -c nginx |
| kubectl logs –previous [pod] | Logs từ instance trước (crash) | kubectl logs –previous crashed-pod |
| kubectl logs –tail=100 [pod] | Last 100 lines | kubectl logs –tail=100 busybox |
| kubectl get events -A | Liệt kê events all namespaces | kubectl get events -A |
| kubectl get events –watch | Watch events realtime | kubectl get events –watch |
| kubectl get events -o yaml | Output YAML chi tiết | kubectl get events -o yaml |
Liên Hệ Với Chứng Chỉ CKAD
Domain Observability (10%) tập trung vào logs và events để debug. Task điển hình:
- Lấy logs từ container cụ thể trong Pod multi-container.
- Sử dụng events để troubleshoot Pod không Running (e.g., ImagePullBackOff).
- Follow logs để xem realtime output trong task deploy.
Mẹo thi:
- Nhớ -c cho multi-container, default lấy container đầu.
- Kết hợp với
describe podđể xem events liên quan. - Thời gian: 3-5 phút/task, dùng autocomplete để nhanh.
- Luyện: Tạo Pod crash và debug bằng logs/events.
- Trong thi, cluster có logs retention ngắn, nên lấy nhanh.
Thực Hành Thực Tế Trên Minikube
Giả sử bạn có Pod nginx từ bài trước.
-
Tạo Pod đơn giản:
kubectl run log-pod --image=busybox --command -- sh -c "while true; do echo 'Log message'; sleep 5; done" -
Giám sát logs:
kubectl logs log-pod # Lấy logs kubectl logs -f log-pod # Follow -
Multi-container logs (từ Bài 8):
kubectl logs sidecar-pod -c app-container kubectl logs sidecar-pod -c logging-sidecar -
Giám sát events:
kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp kubectl get events -A --watch -
Debug crash: Tạo Pod crash:
kubectl run crash-pod --image=busybox --command -- sh -c "exit 1".kubectl describe pod crash-pod # Xem events kubectl logs crash-pod --previous # Logs crash -
Cleanup:
kubectl delete pod log-pod crash-pod.
Nếu không thấy logs, check container running bằng get pods.
Dưới đây là diagram pod logs và events flow, minh họa cách events liên kết với logs cho observability.
Kết Luận
Bài này mình đã hướng dẫn chi tiết giám sát logs và events với kubectl logs cùng các lệnh liên quan, từ cơ bản đến debug. Bạn giờ có thể troubleshoot hiệu quả, sẵn sàng cho domain Observability trong CKAD. Tiếp theo, ở Bài 11: Debug Pod Với kubectl describe Và exec, chúng ta sẽ đi sâu hơn vào các công cụ debug nâng cao.